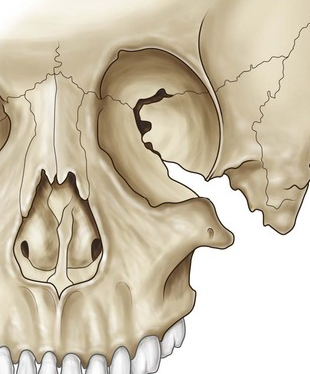
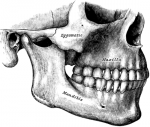
Hypoplasia of the facial bones may be the first indicator of Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS). The cheek (malar or zygomatic) bone is smaller or absent. A cleft in the malar bone is not uncommon.
The malar surface is convex and perforated near its centre by a small aperture, the zygomatic foramen, for the passage of the zygomaticofacial nerve and vessels.
Radiographs and CT may be of value for evaluation of craniofacial abnormalities.
Other symptoms of TCS:
- Mandibular Hypoplasia
- Antimongoloid slanting palpebral fissures
- Lower eye lid coloboma
- malformation of auricles
- External ear canal defect
- Cleft Palate
- Hearing loss
- Visual impairment
- Palate malformation