Most people with a syndrome within the Oculo- Auriculo- Vertebral Spectrum have differences in the size and shape of facial structures between the right and left sides of the face (facial asymmetry). In about two-thirds of cases, both sides of the face have abnormalities, which usually differ from one side to the other. Other individuals are affected on only one side of the face. This is typical for Goldenhar Syndrome. The facial characteristics in Goldenhar syndrome typically include underdevelopment of one side of the upper or lower jaw (maxillary or mandibular hypoplasia), which can cause dental problems and difficulties with feeding and speech. In cases of severe mandibular hypoplasia, breathing may also be affected.
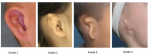
People with Goldenhar syndrome usually have ear abnormalities affecting one or both ears, typically to different degrees. They may have growths of skin (skin tags) in front of the ear (preauricular tags), an underdeveloped or absent external ear (microtia), or a closed or absent ear canal; these abnormalities may lead to hearing loss. Eye problems are less common in Goldenhar syndrome, but some affected individuals have an unusually small eyeball (microphthalmia) or other eye abnormalities that result in vision loss.